Sometimes fridges, especially the old ones, can be real energy hogs. So, if you’re trying to cut down on your power usage or figuring out what size battery backup you need for your fridge, you’ve gotta know how much juice it uses over time. There are a bunch of ways you can figure that out!
What Are Refrigerator Amps?

Understanding the amp requirements helps in managing the overall electrical load in your home. It ensures that the refrigerator does not overload the circuit it is connected to, preventing potential electrical issues. Refrigerator from @ trueresidential
Refrigerator amps indicate the electrical current drawn by its compressor to keep the compartment cool. For most household fridges operating at 120 volts, the amperage typically ranges from 3 to 5. A dedicated circuit of 15 to 20 amps is needed due to the higher initial amperage when the fridge starts up. The average amperage is lower since the compressor isn’t constantly running, often measured in kilowatt-hours (KWH).
Figuring Out How Many Amps Your Fridge Uses
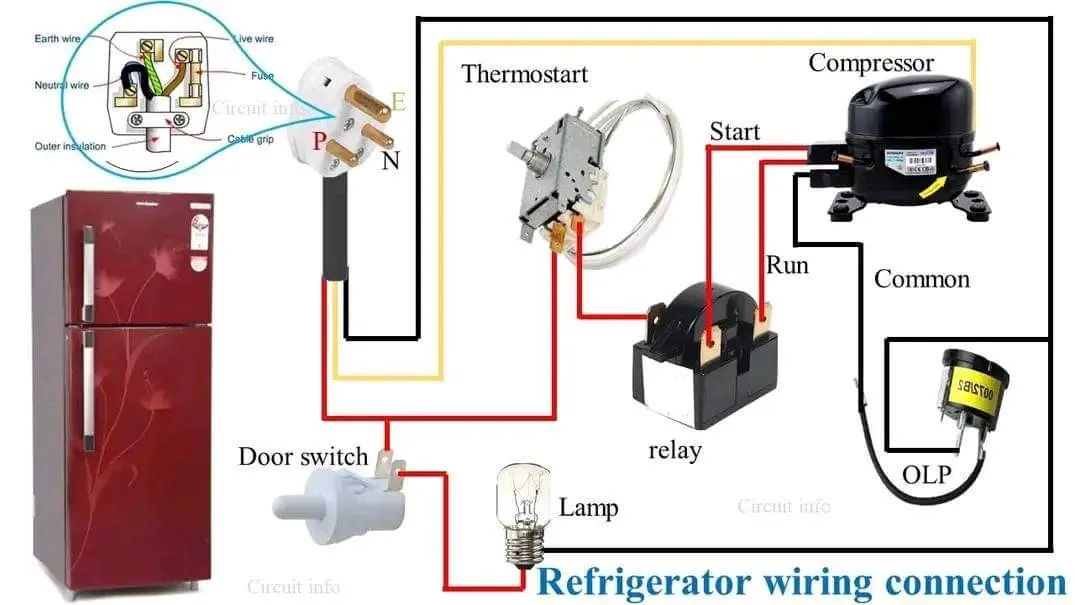
Knowing the amperage ensures that the refrigerator is connected to a circuit with the appropriate breaker. This prevents the circuit breaker from tripping frequently, which can be inconvenient and potentially harmful to the appliance. Refrigerator wiring from @ electricalandelectronicsworld
1. Using Energy Star Ratings to Estimate Fridge Power Usage
The simplest way is to just Google your fridge’s model number and check if it’s got an Energy Star Rating. If it does, you’ll probably find the estimated yearly electricity usage there too.
Here’s a breakdown using an example: Let’s say your fridge’s energy consumption is 227 kWh per year (which equals 227,000 watt-hours per year). If you divide that by the number of days in a year (365), you’ll get approximately 621.91 watt-hours per day (227,000 / 365 = 621.91 Wh). Dividing that by the number of hours in a day (24) gives you an average running power of about 25.91 watts (621.91 / 24 = 25.91). To find the amperage, divide the running watts by the voltage, which is typically 120 volts in the US and Canada. So, taking the average watts of 25.91 and dividing by 120 volts, you get an average of about 0.21 amps (25.91 / 120 = 0.21).
2. Measure Fridge Power Consumption with an Energy Meter

Knowing the amperage ensures that the refrigerator is connected to a circuit with the appropriate breaker. This prevents the circuit breaker from tripping frequently, which can be inconvenient and potentially harmful to the appliance. Refrigerator inspo from @ the_organized_kitchen
If your fridge doesn’t have an Energy Star rating (like many vaccine and commercial fridges), you have a couple of options. You can reach out to the manufacturer to see if they have the energy consumption info. If not, you might consider buying a kWh meter. These devices are handy for accurately measuring power usage. They’re pretty easy to use too—just plug the meter into the wall outlet, then plug your fridge into the meter. It’ll track how much power your fridge is using over time. While they’re not pricey, they can actually help you save money by giving you a better idea of your appliance’s power consumption and how it affects your electric bill.
3. Calculating Fridge Power Consumption Using Nameplate Amperage
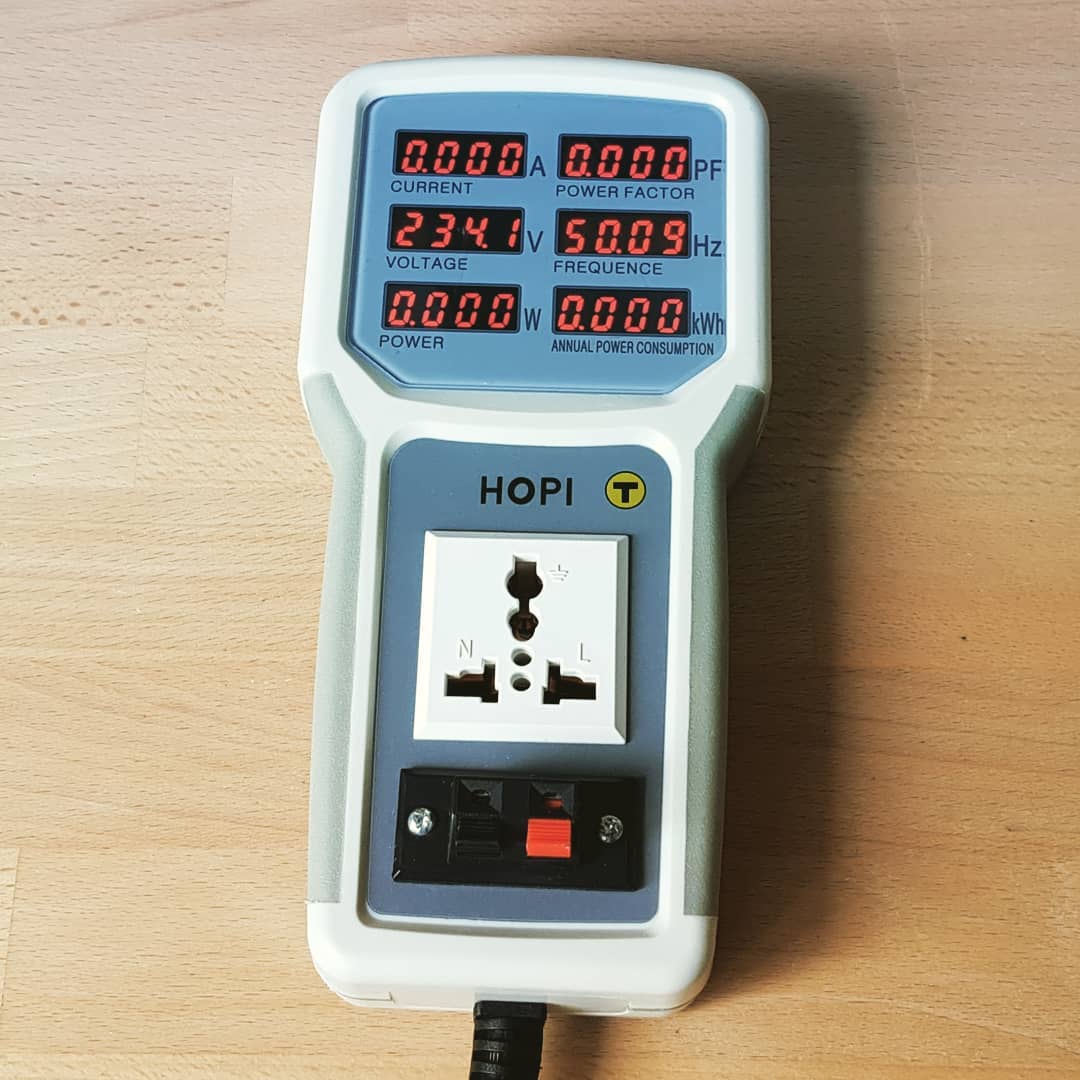

Correctly assessing the amp requirement reduces the risk of electrical fires. Overloading circuits can cause overheating and increase the likelihood of electrical fires, so matching the refrigerator’s needs to the circuit capacity is crucial for safety. Ampere meter from @ derstromiker
Another method is to estimate using the nameplate amperage of the refrigerator. This approach involves a bit of guesswork based on the estimated duty cycle. It’s not as accurate as using a kWh meter, but it can give you a rough idea of the power consumption.
What Is A Duty Cycle?

Knowing the amp usage can help in estimating the energy consumption of the refrigerator. This is useful for budgeting electricity costs and understanding the appliance’s impact on your energy bill. Kitchen appliance from @ dakorkitchen
A fridge compressor doesn’t stay on constantly. It switches on and off. The time the compressor spends running compared to the total cycle time is what we call the duty cycle. The nameplate amperage tells us how many amps the fridge pulls when the compressor is running, but because of the duty cycle, the actual average amperage is usually lower than the nameplate value.
Different fridges have different efficiencies, affected by factors like insulation. Typically, a fridge runs on a 35% duty cycle (65% for a freezer). So, if you take the nameplate amperage and divide it by 35%, you can estimate the average running amps.
For example: if the nameplate amperage is 4 amps, and the duty cycle is 35%, the average running amperage would be around 1.4 amps.
Other Things to Consider

Proper installation of the refrigerator may require knowing its electrical specifications. This includes ensuring that the outlet and wiring meet the required standards for the appliance’s safe operation. Appliances from @ kristywicks
As mentioned before, newer appliances are way more efficient than older ones. If your appliance is over 15 years old, getting a newer model will likely save you money in a few years just from energy savings alone, not to mention the expected repair costs.
If buying a new appliance isn’t in the cards, another way to cut down on your refrigerator’s power use is to keep up with maintenance. Simple stuff like cleaning the coils and checking the seals can make a big difference in energy savings.
















